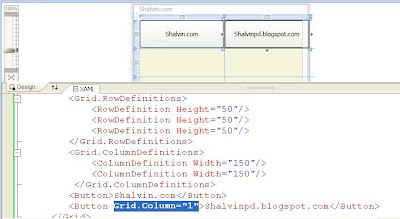
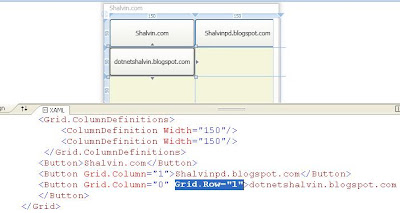
If an element uses a binding expression and its DataContext property is null the element continues its search up the element tree. This search continues until the element finds a data object or reaches the toplevel container, which is the user control that represents the page.
DataSet is an offline disconnected data store. A DataSet can be constructed using the Fill method of SqlDataAdapter.
using System.Data;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
SqlConnection cnn;
SqlDataAdapter da;
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
private void Window_Loaded(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
cnn = new SqlConnection(@"Data Source=.\sqlexpress;Integrated Security=sspi;Initial catalog=AirLines");
da = new SqlDataAdapter("select * from Location", cnn);
da.Fill(ds, "Loc");
LayoutRoot.DataContext = ds.Tables["Loc"];
}
<Grid Name="LayoutRoot">
<ListBox ItemsSource="{Binding}"
DisplayMemberPath="LocationName"
Height="100" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="10,10,0,0" Name="listBox1" VerticalAlignment="Top" Width="120" />
</Grid>
Binding to DataGrid
<Grid Name="LayoutRoot">
<DataGrid ItemsSource="{Binding}" AutoGenerateColumns="True" Height="150" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="17,13,0,0" Name="dataGrid1" VerticalAlignment="Top" Width="325" />
</Grid>
WPF DataGrid Custom Columns
<Grid Name="LayoutRoot">
<DataGrid ItemsSource="{Binding}" AutoGenerateColumns="False" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="42,12,0,0" Name="dataGrid1" Width="296">
<DataGrid.Columns>
<DataGridTextColumn Header="Serial No" Binding="{Binding LocationId}" />
<DataGridTextColumn Header="Location Name" Binding="{Binding LocationName}" />
<DataGridTextColumn Header="Latitude" Binding="{Binding Latitude}" />
<DataGridTextColumn Header="Longitude" Binding="{Binding Longitude}" />
</DataGrid.Columns>
</DataGrid>
</Grid>
{Binding LocationName} is the shorthand to {Binding Path=LocationName}